Vacancy is one of the biggest challenges for rental property owners.
Every day your property is vacant means lost income, yet the expenses keep coming—taxes, insurance, and maintenance don’t take a break. Over time, high vacancy rates can quietly erode your profits and stall the growth of your investment.
That’s why understanding and managing your vacancy rate is crucial. This comprehensive guide will walk you through what rental vacancy rates are, how to calculate them, and most importantly, practical strategies to keep your properties occupied and your cash flow steady.
If you’re serious about maximizing your rental income, minimizing vacancy should be your top priority. If you want to read on all the factors that can increase your rental income, check out our complete article on it.
Understanding Rental Vacancy Rate
The vacancy rate is a simple but important way to see how often your rental property sits empty, costing you money. It shows the percentage of time that your property—or a group of properties—goes without earning rent.
For example, if you own 10 rental units and one is currently vacant, your vacancy rate is 10%. If you own one rental property that stays empty for 30 days out of the year, your vacancy rate would be around 8%. The more time your property is empty, the higher your vacancy rate, and the more money you’re missing out on.
In short, the vacancy rate gives you a clear picture of how often your property isn’t earning income, helping you see if changes are needed to keep it rented out consistently.
It’s typically measured on a yearly basis, but it can also be calculated monthly or quarterly depending on the needs of the investor.
Why is the Vacancy Rate Important for Rental Property Investors?
For rental property investors, vacancy rate matters because every day a property sits vacant is a day it isn’t generating income. It doesn’t matter how good the rent is, how well-maintained the property is, or how prime the location might be—if a property is vacant, it’s losing money.
Understanding the vacancy rate helps investors:
- Gauge market health: A higher-than-usual vacancy rate in a particular area might indicate weak resident demand or market saturation.
- Optimize rental pricing: High vacancy rates might suggest your rental prices are too high for the market, while lower rates could indicate that you’re pricing competitively.
- Assess portfolio performance: Tracking vacancy rates across a portfolio helps you identify which properties are performing well and which ones need adjustments, whether through marketing, pricing, or upgrades.
The vacancy rate directly affects profitability and cash flow, making it a key performance metric for any real estate investor.
Impact on Rental Income and Profitability
Vacancy rates have a profound impact on cash flow.
Consider this: if you own a rental property that generates $1,500 in monthly rent, but it’s vacant for one month, that’s $1,500 in lost revenue.
However, the operating expenses—such as rental property taxes, insurance, and maintenance—don’t stop. This means that a high vacancy rate can lead to negative cash flow, where the expenses outweigh the rental income.
The lower the vacancy rate, the more consistent the rental income, which stabilizes your portfolio and helps you plan for future investments. A vacancy rate that consistently stays below market average gives you a competitive edge in the rental market.
Common Misunderstandings
- Confusing Vacancy Rate with Occupancy Rate: Some people mix up these two terms. The occupancy rate is the opposite of the vacancy rate, representing the percentage of occupied rental properties, not vacant ones. So, if the vacancy rate is 10%, the occupancy rate is 90%.
- Including Non-Marketable Properties in the Calculation: Some landlords mistakenly include properties that are not available for rent (e.g., undergoing renovations) in their vacancy rate calculation. The official vacancy rate only includes marketable properties that are ready and available for residents.
- Confusing Vacancy with Turnover: The vacancy rate refers to how often a property is empty, while the turnover rate refers to how often residents move out. A property could have high residents turnover but low vacancy if new residents move in quickly.
The Different Ways of Looking at Vacancy Rates
Vacancy rates can be viewed from different angles depending on what you want to analyze. Whether you’re looking at an entire area, a single property, or your entire portfolio, each calculation offers specific insights.
These distinctions matter because they help you understand the health of the rental market, the performance of individual units, and the overall efficiency of your portfolio management.
Knowing how to interpret these different rates allows you to make more informed decisions about pricing, marketing, and property management.
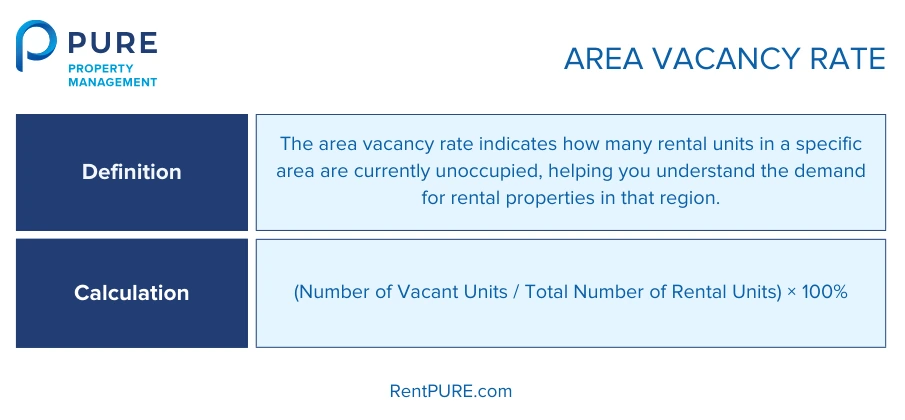
1. Area Vacancy Rate
The area vacancy rate tells you how many rental units in a particular area are currently vacant. This is important because it helps you see how much demand there is for rental properties in that region.
If the area has a high vacancy rate, it might mean there are too many available units and not enough people looking to rent. On the other hand, a low vacancy rate means demand is high, and properties get rented out quickly.
To get this percentage, you divide the number of vacant units by the total number of rental units in the area, and then multiply by 100 to get a percentage.
Here’s how the formula works:
- Vacant Units: This is the number of properties that are currently empty in the area.
- Total Rental Units: This counts all the rental units that could potentially be rented out.
When you divide the number of vacant units by the total units, you’ll get the percentage of properties that are currently unoccupied—your vacancy rate.
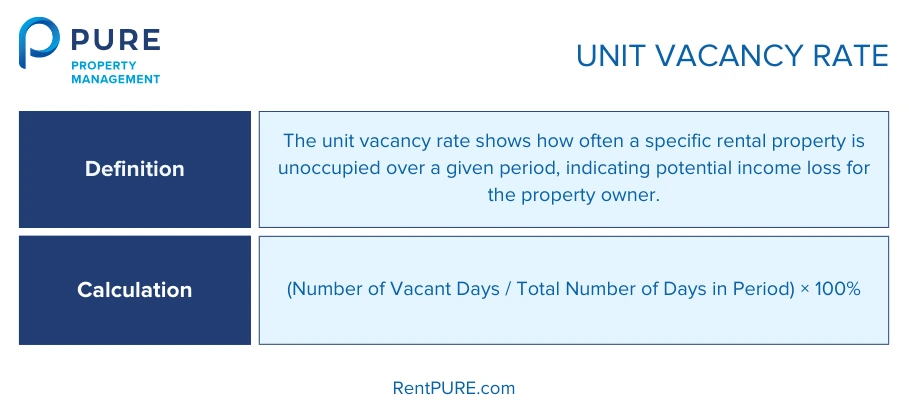
2. Unit Vacancy Rate
The unit vacancy rate helps you figure out how long a specific rental property is sitting empty over a certain period, usually one year. If a rental unit isn’t occupied for a big chunk of the year, it’s not bringing in any income, which is a problem for any property owner.
To calculate this, you take the number of days the unit was vacant and divide it by the total number of days in the period (usually 365 days in a year). Multiplying by 100 gives you the vacancy rate as a percentage.
Here’s how the formula works:
- Vacant Days: These are the days when your property was not rented out.
- Total Days in the Period: This is usually 365 days for a full year, but you can use a shorter period if needed (e.g., 30 days for a month).
Calculating the number of vacant days against the total days shows how long the property has been sitting empty over the year.
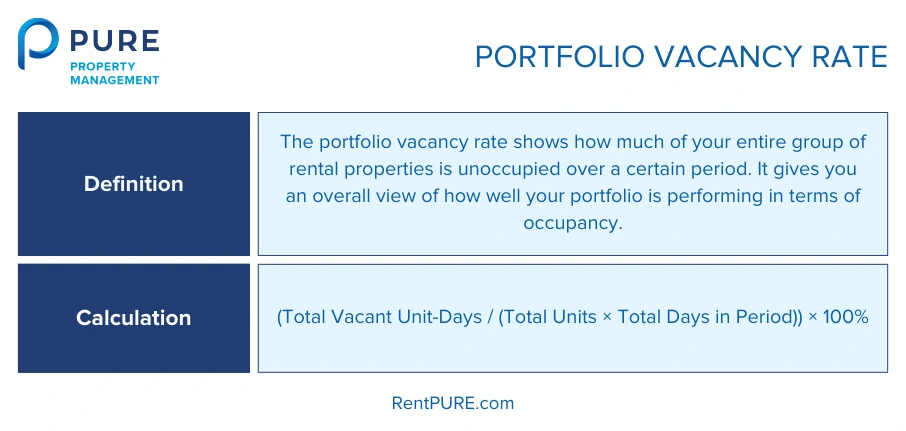
3. Portfolio Vacancy Rate
If you own multiple properties, the portfolio vacancy rate lets you see how your entire group of properties is doing. It’s like zooming out to get the big picture. Instead of looking at one property, this rate tells you how much of your entire rental portfolio was empty over a certain period.
To calculate this, you need to add up all the vacant days from each unit, then divide that by the total number of units multiplied by the total number of days in the period (usually a year). Multiplying by 100 gives you the percentage.
Here’s how the formula works:
- Total Vacant Unit-Days: This is the sum of all the vacant days for each unit. So, if you have 3 properties, and one was vacant for 10 days, another for 20 days, and a third for 5 days, you add those up (10 + 20 + 5 = 35 vacant unit days).
- Total Units × Total Days in Period: This is the total number of days all your units were available for rent. If you have 5 units and you’re calculating for one year, it’s 5 units × 365 days = 1,825 unit-days.
By comparing the total number of vacant days (of all vacant properties during the given period) with the total available days (of all available units), you’ll see the overall percentage of time your portfolio has been unoccupied.
Why These Rates Matter
Each of these rates—area, unit, and portfolio vacancy rates—tells you something different about your rental business:
- Area Vacancy Rate: Helps you understand the market conditions and whether you’re in a competitive rental area.
- Unit Vacancy Rate: Helps you assess how well individual properties are performing, so you can fix any issues that cause frequent vacancies.
- Portfolio Vacancy Rate: Gives you an overview of how your entire rental business is doing, helping you make strategic decisions for long-term success.
Regularly calculating these rates helps you spot issues early, reduce vacancy periods, and boost your profits.
How to Calculate Rental Vacancy Rates (with examples)
Understanding how to calculate vacancy rates is key to managing your rental properties effectively.
We’ll go through each type of vacancy rate—whether you’re looking at the overall market, a single unit, or your entire portfolio—and explain how to calculate them.
With clear examples, you’ll gain a better understanding of how each calculation can help you make informed decisions about your properties and ensure you’re minimizing vacancies and maximizing returns.
1. Calculating Area Vacancy Rate
The area vacancy rate helps you understand how many rental units in a particular geographic region are currently vacant. It’s useful for analyzing demand in the area—higher rates might signal oversupply, while lower rates indicate stronger demand.
Step-by-Step Example:
Imagine you’re analyzing a small neighborhood that has 500 rental units, of which 25 are currently vacant.
- Identify Vacant Units: There are 25 units currently vacant.
- Total Rental Units: The neighborhood has 500 rental units in total.
- Apply the Formula:
Area Vacancy Rate = (Number of Vacant Units / Total Number of Rental Units) × 100
Area Vacancy Rate = (25 / 500) × 100 = 5%
This result shows that 5% of the rental units in this area are vacant. This rate helps you gauge the health of the local rental market, indicating whether properties are being filled quickly or if there’s excess supply.
2. Calculating Unit Vacancy Rate
The unit vacancy rate measures how long an individual rental property is vacant over a certain period, usually a year. This rate helps property owners understand how well a specific property is performing.
Step-by-Step Example:
Let’s say you have a single property that was vacant for 45 days out of the year.
- Identify Vacant Days: The property was vacant for 45 days.
- Total Days in the Year: The total number of days in the year is 365.
- Apply the Formula:
Unit Vacancy Rate = (Number of Vacant Days / Total Number of Days in Period) × 100%
Unit Vacancy Rate = (45 / 365) × 100 ≈ 12.33%
A 12.33% vacancy rate indicates that the property was unoccupied for a notable portion of the year. You may want to investigate whether pricing, maintenance, or marketing improvements are needed to keep the unit rented for a larger part of the year.
3. Calculating Portfolio Vacancy Rate
The portfolio vacancy rate shows the overall vacancy across all your properties, giving you a big-picture view of your rental business.
Step-by-Step Example:
Imagine you own three properties:
- Property A: 2 units, 1 unit vacant for 50 days.
- Property B: 4 units, 2 units vacant for 30 days each.
- Property C: 1 unit, vacant for 10 days.
1. Calculate Total Possible Rental Days
First, we need to figure out how many total days your units were available for rent over the year. We do this by multiplying the number of units by the total days in the period (usually 365 days).
- Property A: 2 units × 365 days = 730 unit-days
- Property B: 4 units × 365 days = 1,460 unit-days
- Property C: 1 unit × 365 days = 365 unit-days
Total Possible Rental Days:
730 + 1,460 + 365 = 2,555 unit-days
This means that if all your units were occupied every day of the year, they would generate 2,555 days of rental time.
2. Calculate Total Vacant Unit-Days
Next, we calculate how many days each unit was vacant and then add them up.
- Property A: 1 unit × 50 days = 50 unit-days
- Property B: 2 units × 30 days = 60 unit-days
- Property C: 1 unit × 10 days = 10 unit-days
Total Vacant Days:
50 + 60 + 10 = 120 unit-days
This shows that across all properties, your units were vacant for a total of 120 days.
3. Apply the Formula
Finally, we use the formula to calculate the portfolio vacancy rate:
Portfolio Vacancy Rate = (Total Vacant Unit-Days / Total Possible Rental Days) × 100
Portfolio Vacancy Rate = (120 / 2,555) × 100 ≈ 4.70%
This means that 4.7% of your total available rental days were unoccupied, giving you an overall view of how your properties are performing.
This 4.70% vacancy rate across your portfolio is a solid indication that your properties are performing well overall, but you may want to investigate any patterns in vacancies to make further improvements.
Calculating vacancy rates for different levels—whether for an area, an individual property, or an entire portfolio—provides critical insights into the performance and profitability of your rental business.
Regularly applying these formulas ensures you can address potential issues early, optimize your rental strategy, and keep your properties occupied.
What is a Good Vacancy Rate?
There is no universal number for what makes a “good” vacancy rate—it can vary significantly based on location, property type, and market conditions.
As a rule of thumb, the lower your vacancy rate, the better your rental business is performing. The ideal vacancy rate for any investor is zero percent (which is virtually impossible to achieve).
However, understanding industry benchmarks can provide useful context, allowing you to gauge whether your property is performing well or if improvements are needed.
According to the U.S. Census Bureau, the national average vacancy rate for rental property currently stands at 6.6%, providing a useful benchmark for comparing local and property-specific vacancy rates.
If your vacancy rate is lower than the average number in your area, you’re in the clear. If it’s higher, you need to do something about it (we talk more about this later in the article).
Industry Benchmarks and Averages
- Urban Areas: In busy cities with high rental demand, vacancy rates tend to be lower. This is because more people are looking for housing, and properties tend to get rented out quickly. If your property is in an urban area and your vacancy rate exceeds this range, it could signal a problem with pricing, marketing, or property condition.
- Suburban and Rural Areas: Properties located outside major cities tend to have higher vacancy rates. These areas usually have fewer renters, meaning properties may sit vacant for longer periods. However, if you find your rate exceeding 7%, it’s worth revisiting your strategy to attract and retain residents.
- Seasonal Properties: Vacation rentals and properties in tourist-heavy areas often have higher vacancy rates, especially during off-seasons. In these cases, vacancy rates can spike well beyond what’s typical for urban or suburban properties. The key here is balancing high rental income during peak seasons with the reality of longer vacancy periods during quieter months.
Factors Influencing a “Good” Vacancy Rate for Your Property
A vacancy rate that works for one property or area may not work for another, which is why it’s important to factor in the specific characteristics of your property and its market. Here are the major factors that influence what’s considered a “good” vacancy rate:
- Rental Demand in Your Area: Areas with high rental demand, such as near universities, business districts, or transportation hubs, will typically have lower vacancy rates. If your property is in one of these areas but you’re experiencing high vacancies, it could point to issues that can be addressed, such as poor marketing or an outdated property.
- Property Condition: Well-maintained properties are far more likely to attract residents and retain them over the long term. If your vacancy rate is higher than average, assessing the condition of your property is a critical first step. Regular maintenance, modern amenities, and curb appeal all play a role in keeping units occupied.
- Rental Pricing: Competitive pricing is crucial. If your rent is too high compared to similar properties in the area, your vacancy rate will likely increase as potential residents look elsewhere. Research comparable properties (also known as “comps”) to ensure you’re not pricing yourself out of the market. Adjustments to pricing—even a small reduction—can often result in faster leasing.
- Marketing Efforts: A strong marketing strategy is key to keeping vacancy rates low. If you’re not reaching enough potential renters, or if your listings don’t stand out, your property could sit vacant longer. Invest in high-quality photos, write detailed and engaging descriptions, and use multiple platforms to advertise. Consider targeted advertising on social media, as well.
- Seasonality: Some areas experience significant rental fluctuations based on the time of year. For example, student housing markets may see higher vacancy rates during the summer months when students are away. Understanding these seasonal trends and planning for them—such as adjusting rent prices or offering shorter leases—can help keep your property occupied even during off-peak times.
How to Research Local Vacancy Rates
To make informed decisions, you need to know what vacancy rates are like in your local market. Here’s how you can start gathering that data:
- Look at Local Market Reports: Many real estate websites and platforms like Zillow, Apartments.com, or Rent.com offer market reports that provide insights into vacancy rates in specific areas. These can be useful for understanding trends in your city or neighborhood.
- Consult with Local Property Managers: If you’re unsure about how to research vacancy rates, local property managers can often provide valuable insights. They typically have access to data on local market trends and can give you a clearer picture of what vacancy rates are common in your area.
- Use Census Data: Government websites, such as the U.S. Census Bureau, provide data on rental vacancy rates at the national, state, and local levels. This can be helpful in understanding broad trends, though it may not provide granular, up-to-date information.
- Talk to Real Estate Agents: Real estate agents who specialize in rental properties often have a deep understanding of vacancy trends and can help you assess whether your property’s performance aligns with the market.
Once you’ve gathered data, compare your property’s vacancy rate to these local benchmarks. If you find your rate is higher than the area average, it’s a good signal to revisit your property management, pricing, and marketing strategies.
How to Reduce Vacancy Rate in Rentals
Keeping vacancy rates low is critical for maintaining a steady flow of rental income.
To achieve this, landlords need to take proactive steps both before renting out the property and during the residency. These strategies will help you attract quality residents, retain them longer, and keep your rental business running smoothly.
Before Renting: Setting the Foundation for Success
To minimize vacancy, the work starts long before a resident moves in. How you prepare your property and market it will significantly impact how quickly it gets rented.
Taking a proactive approach ensures your property stands out and attracts high-quality residents who are more likely to stay long-term.
-
Boost Curb Appeal
First impressions can significantly influence a renter’s decision. If the exterior of your property looks inviting, potential residents are more likely to consider renting it.
Simple improvements, like fresh paint, well-maintained landscaping, and new fixtures, make a huge difference. When renters feel good about a property from the moment they see it, they’re more likely to view it as their potential home.
-
Invest in Upgrades and Refurbishing
Small upgrades can dramatically improve your property’s appeal and value. Well-maintained properties with modern features typically attract higher-quality residents and stay rented longer.
Focus on upgrades that offer the most value, such as energy-efficient windows, updated kitchen appliances, fresh flooring, or small enhancements like updated light fixtures and door hardware. These changes can set your property apart from the competition, enhance its appeal, and help reduce vacancy periods.
-
Optimize Your Marketing Strategy
Even the best property can sit vacant if no one knows about it. Effective marketing ensures that your property gets the attention it deserves from the right audience.
Use professional photos, write compelling descriptions, and list your property across multiple platforms. A well-marketed rental attracts more inquiries and reduces the time your unit stays vacant.
-
Screen Residents Carefully
Selecting reliable residents is crucial for minimizing vacancy and ensuring long-term income. Careful resident screening helps avoid residents who may leave prematurely or cause problems.
Verify resident history, credit, and references. This helps ensure you’re renting to people who are responsible, pay rent on time, and will take care of the property—ultimately reducing turnover and vacancy.
-
Set Competitive Rental Pricing
Overpricing your property can lead to longer vacancy periods, while underpricing it means losing out on potential income. Striking the right balance is key.
Conduct market research to determine fair and competitive pricing. Look at similar properties in your area to ensure your rent attracts potential residents while still maximizing your profit.
While the Property is Occupied: Maintaining Resident Satisfaction
Once your property is rented, keeping residents satisfied is key to reducing turnover. A focus on property maintenance, communication, and lease flexibility helps ensure residents stay longer, reducing the costs and downtime associated with vacancies.
-
Keep Up with Property Maintenance
Residents are far more likely to stay in a property that is well-maintained and problem-free. Regular maintenance keeps your property in top shape and residents satisfied.
Address repairs promptly and consider a preventive maintenance schedule to keep things running smoothly. Well-maintained properties not only attract residents but also encourage them to renew their leases.
-
Maintain Open and Responsive Communication
Good communication builds trust and helps you stay ahead of resident issues. Residents who feel heard and respected are more likely to remain in the property long term.
Make yourself accessible and responsive. Whether it’s handling maintenance requests or addressing concerns, timely communication reassures residents that they are in good hands.
-
Offer Lease Renewal Incentives
Offering perks for lease renewals can encourage residents to stay longer. Simple incentives can be the deciding factor in convincing residents to renew.
Consider providing upgrades like new appliances, offering a discount on the first month of their renewed lease, or including a free cleaning service. These incentives cost less than finding new residents and help keep your property occupied.
-
Provide Flexible Lease Terms
Not every resident wants a one-year lease. Offering flexible options, like six-month or month-to-month terms, can open your property to a wider pool of residents.
This flexibility can be particularly useful in areas with seasonal demand or for residents who are unsure about long-term commitments. It allows you to meet resident needs while reducing vacancy gaps.
-
Build Strong Relationships with Residents
Residents who feel appreciated are more likely to stay. Simple gestures like checking in, addressing their concerns quickly, and being approachable can foster a positive relationship.
Building a strong relationship with your residents doesn’t require much effort, but it can significantly reduce turnover. Happy residents are more likely to renew and take care of the property.
-
Consider Hiring a Professional Property Manager
Managing multiple properties can become overwhelming, especially when it comes to resident communication, maintenance, and marketing. A professional property manager can handle these tasks, ensuring your properties are well-managed and vacancies minimized.
A property manager not only handles resident relations but also streamlines maintenance and helps with marketing and pricing strategies. They can reduce vacancy by providing expert oversight, giving you peace of mind and more time to focus on other aspects of your investment.
The Impact of High Vacancy Rates On Your Rental Business
High vacancy rates can seriously affect the profitability of your rental business. When units remain empty for extended periods, they don’t generate any income, leading to financial strain and reduced cash flow.
Beyond lost rent, high vacancies can also mean higher maintenance costs and a negative impact on your property’s reputation. Understanding and managing vacancy rates is essential to keep your rental properties profitable and your business thriving.
Loss of Rental Income
This is the most obvious and direct impact of high vacancy rates. Every day that your rental property is vacant is a day you are losing out on rental income. Over time, extended vacancies can result in a serious financial shortfall.
Increased Marketing Costs
Vacant properties require additional marketing efforts to find new residents. Whether you’re paying for online advertisements, hiring photographers to take new listing photos, or investing in staging the property for viewings, these costs add up, eating into your profits.
Property Deterioration
A vacant property is more likely to experience deterioration. Without regular use, minor issues like leaks, electrical problems, or pest infestations can go unnoticed and worsen over time. Additionally, properties that sit empty for long periods of time are more prone to vandalism or break-ins, increasing your risk of costly repairs.
Negative Impact on Portfolio Valuation
For investors with multiple properties, high vacancy rates can negatively affect the value of the entire portfolio. A portfolio with consistently high vacancy rates is seen as riskier, which can make it more difficult to secure financing or sell properties for top dollar.
In Conclusion
Managing vacancy rates is one of the most important aspects of owning and operating rental properties. A high vacancy rate not only means lost income, but it also affects your overall profitability, increases your expenses, and can lower the value of your investment over time. Understanding your vacancy rate and knowing how to control it is crucial for staying competitive in the rental market.
In this guide, we’ve covered key aspects of vacancy rates and how they impact your rental business:
- What Vacancy Rates Are: Vacancy rates measure the percentage of time your property or portfolio is unoccupied, providing insight into your rental income.
- Why They Matter: High vacancy rates lead to lost income and ongoing expenses, while low vacancy rates indicate strong rental performance.
- Different Types of Vacancy Rates: We explored three perspectives: Area Vacancy Rate (market-wide), Unit Vacancy Rate (individual properties), and Portfolio Vacancy Rate (across all your properties).
- How to Calculate Them: Step-by-step instructions and examples helped clarify how to calculate each type of vacancy rate.
- What Constitutes a Good Vacancy Rate: Benchmarks and averages based on property type and location, including national standards like the U.S. Census Bureau’s 6.6% average.
- Researching Local Vacancy Rates: Practical steps for gathering vacancy data in your market to help guide your rental pricing and marketing strategies.
- Strategies to Minimize Vacancy Rates: Actionable tips for keeping properties occupied, such as improving curb appeal, setting competitive rental prices, using effective marketing, and maintaining strong relationships with residents.
Regularly calculating your vacancy rates and comparing them to industry benchmarks gives you valuable insights into your properties’ performance. This allows you to take proactive steps to lower vacancies, such as improving property conditions, adjusting rental pricing, or offering flexible lease terms.
Managing resident relationships and responding quickly to issues can help retain residents, further reducing vacancy periods. If managing multiple properties becomes overwhelming, hiring a professional property manager can be an effective solution for streamlining operations and maximizing occupancy.
Keeping your vacancy rate low is critical to maintaining a healthy, profitable rental business. With the right approach, you can ensure that your properties remain occupied and continue generating consistent income, protecting your investment for the long term.
Vacancy rates aren’t the only thing impacting your rental income. Here are some other things you should know about so you can maximize your revenue:








